Temperature measurement is critical in many industrial and scientific applications, and RTDs are among the most reliable sensors for this purpose. Among the various types of RTD sensors, PT100 sensors are known for their accuracy and reliability. However, choosing the right PT100 sensor involves understanding the differences between 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire configurations. This article will guide you through these options, helping you select the best RTD sensor for your needs.
Understanding RTD Sensors
RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) sensors measure temperature by correlating the resistance of the RTD element with temperature. PT100 sensors, specifically, have a resistance of 100 ohms at 0°C. As the temperature changes, the resistance changes in a predictable manner, allowing for precise temperature measurement. RTD sensors, including PT100, are valued for their stability, repeatability, and wide temperature range.
The Basics of PT100 Sensors
PT100 sensors are platinum-based RTDs known for their high accuracy and linearity. The “100” in PT100 indicates the sensor’s resistance at 0°C, which is 100 ohms. Due to their robustness and accuracy, these sensors are widely used in various industries. However, the wiring configuration plays a critical role in their performance.
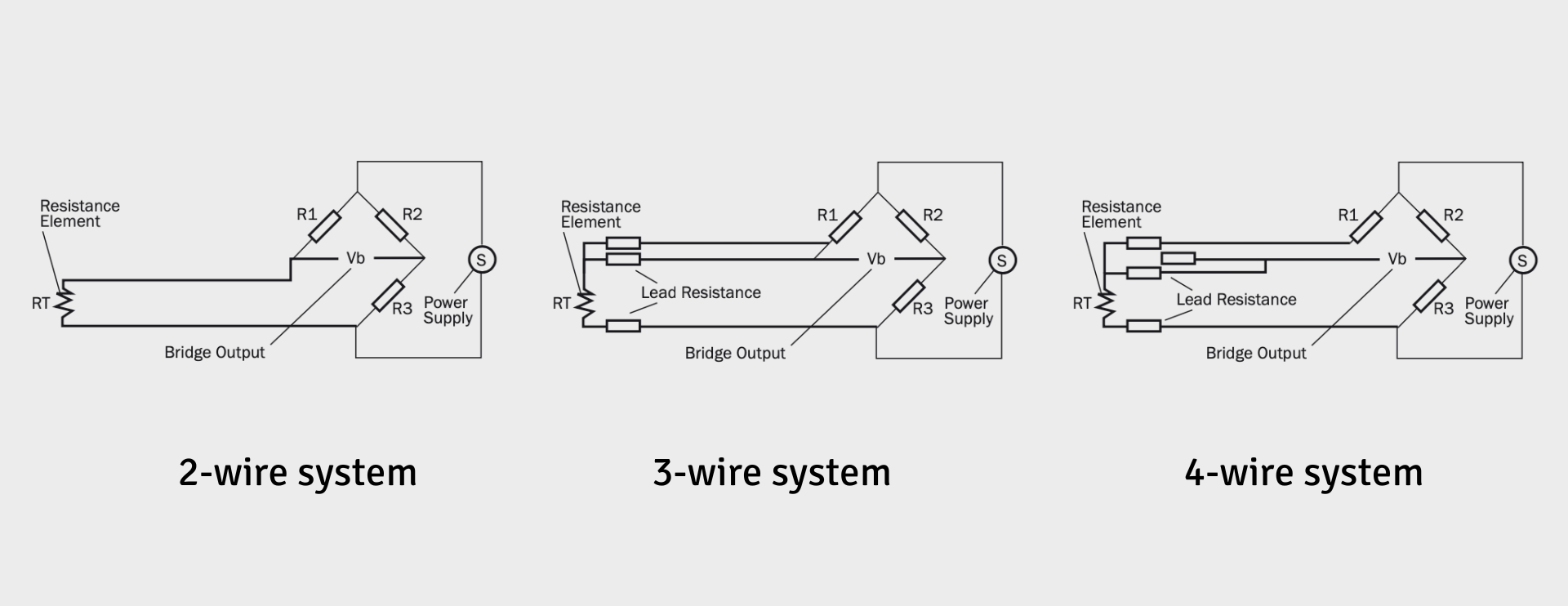
2-Wire PT100 Sensors
Configuration and Working Principle:
A 2-wire PT100 sensor is the simplest form, with two wires connected to the sensor element. A constant current is passed through the RTD, and the voltage drop is measured to calculate the resistance.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
The main advantage of 2-wire PT100 sensors is their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, they are less accurate due to the resistance of the connecting wires, which can lead to measurement errors, especially over long distances or in varying temperature conditions.
Applications:
2-wire PT100 sensors are suitable for applications where high accuracy is not critical and where the environment is relatively stable.
3-Wire PT100 Sensors
Configuration and Working Principle:
A 3-wire PT100 sensor adds an extra wire, with two wires connected to one end of the RTD and the third wire connected to the other end. This configuration helps compensate for the resistance of the lead wires.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
3-wire PT100 sensors offer improved accuracy compared to 2-wire sensors by compensating for the lead wire resistance. However, they are still slightly less accurate than 4-wire sensors.
Applications:
These sensors are commonly used in industrial applications where moderate accuracy is sufficient, and they offer a good balance between cost and performance.
4-Wire PT100 Sensors
Configuration and Working Principle:
A 4-wire PT100 sensor is the most accurate configuration. It uses two wires to carry the current and two separate wires to measure the voltage drop across the RTD element, eliminating the effect of lead wire resistance.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
The main advantage of 4-wire PT100 sensors is their high accuracy and precision. They are ideal for applications requiring the highest accuracy. The downside is the increased complexity and cost.
Applications:
4-wire PT100 sensors are used in laboratory settings and high-precision industrial applications where the highest accuracy is required.
Choosing the Right RTD Sensor
When choosing between 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire PT100 sensors, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy Requirements: For applications requiring high precision, a 4-wire PT100 sensor is the best choice. For moderate accuracy, a 3-wire sensor is suitable, while 2-wire sensors are adequate for less critical applications.
- Budget: 2-wire sensors are the most cost-effective, followed by 3-wire and 4-wire sensors.
- Application Needs: Consider the specific needs of your application. For example, in environments with long cable runs or varying temperatures, a 3-wire or 4-wire sensor may be more appropriate.
Use Case Examples:
- 2-Wire PT100: Basic industrial processes where precise temperature control is not critical.
- 3-Wire PT100: General industrial applications with moderate accuracy requirements.
- 4-Wire PT100: Laboratory research and high-precision manufacturing processes.
Selecting the right RTD temperature sensor configuration is extremely important for accurate and reliable temperature measurement. By understanding the differences between 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire PT100 sensors, you can make an informed decision that meets your specific needs.
Whether you need a cost-effective solution or the highest level of accuracy, there is a PT100 sensor configuration that will fit your requirements.
Explore your options and ensure optimal performance in your temperature measurement applications with the right PT100 RTD sensor.




